Case Studies of Cities Heavily Impacted by Smog from Vehicle Emissions
Air pollution remains a top-notch environmental and public health issue that affects the world. Of all the categories of smog, the most acute problem is the one referred to as smog, plaguing large cities the most. Road transport is one of the leading sources of pollution due to its NOx, CO, and PM2.5 emissions to the atmosphere.
This paper examines scenarios of cities highly affected by smog from vehicle emissions, such as Los Angeles, Delhi, and Beijing, and the causes, effects, and measures taken by each. In doing so, we will discuss related topics and present various statistics and opinions on how other cities can benefit from these best practices.
Smog and Contribution of Vehicle Emissions:
Understanding Smog
Smog is a blend of air pollutants, evident overseas, and hazy air over cities and large metropolitan cities. There are two main types of smog:
● Photochemical Smog: A ground-level ozone formed by the reaction of sunlight with other emissions such as NOx and volatile organic compounds.
● Sulfurous Smog: Burning fossil fuels such as coal releases sulfur oxide, especially sulfur dioxide (SO₂).
Contribution of Vehicle Emissions
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Emissions from combustion engines. These are the precursors to known air pollutants such as ozone and particulate matter.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Released from the evaporation of fuel and car exhaust pipes, these combine with sunlight to produce smog.
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5): Very small droplets that can reach the inner parts of the respiratory system in humans, thus being dangerous.
Effects of Automobile Exhausts on Smog Around the World
Health Impacts
- Respiratory Issues: Long-term exposure to smog raises the susceptibility of newborns to asthma, bronchitis, and lung infections.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Smog exacerbates the conditions that cause heart attacks and strokes because of the actions it has on the blood vessels.
- Premature Deaths: The WHO approximates that outdoor air pollution and smog directly lead to the death of over 4.2 million people every year.
Environmental Impacts
- Crop Damage: Ozone in smog inhibits processes of photosynthesis in plants, which in turn reduces crop yields on the plants.
- Climate Change: Some emissions, such as carbon, cause the sun’s heat to be absorbed, leading to an increase in the greenhouse effect.
Case Study 1: Los Angeles, USA
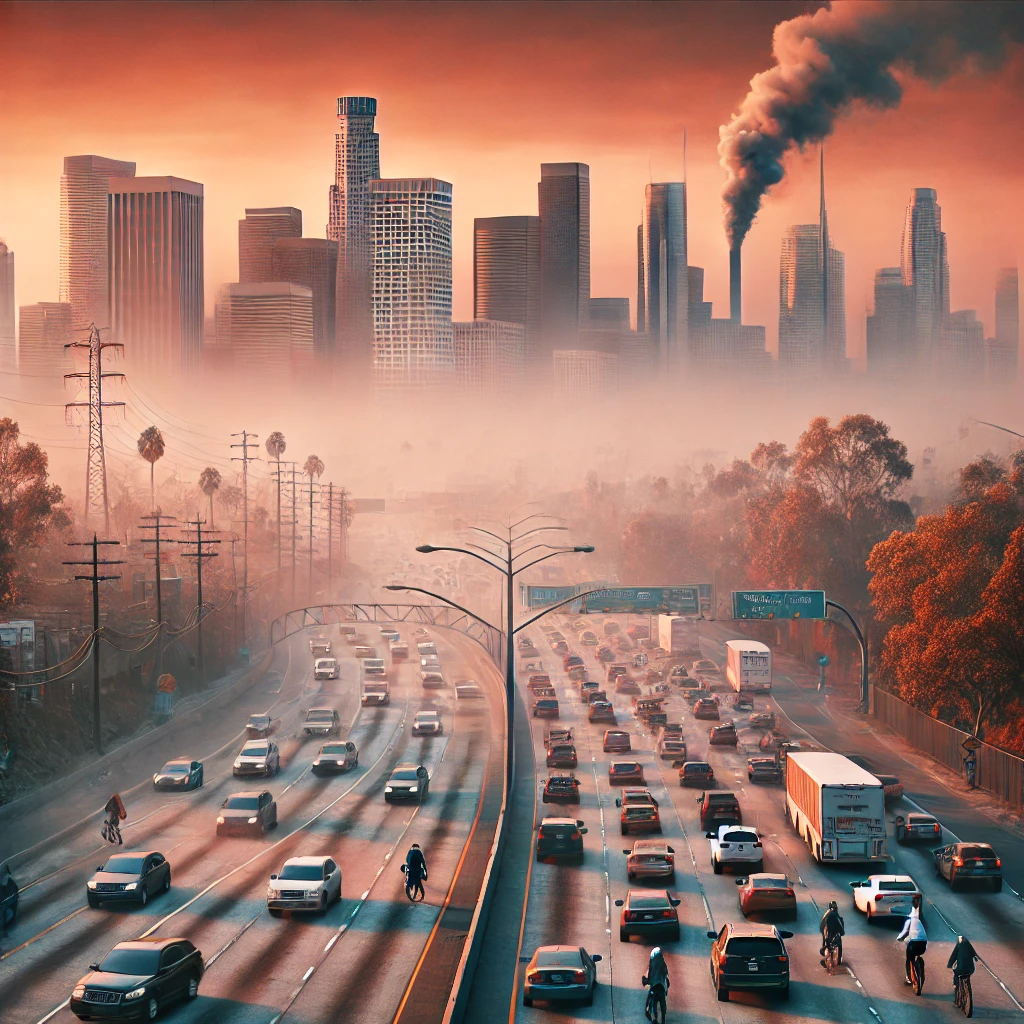

Overview:
Los Angeles is one of the cities that have been researched the most regarding its smog problem. It was nicknamed the Smog Capital of the World in the mid-twentieth century. The disadvantage of this region is the geographic location, a basin surrounded by mountains that represent the means for pollutants to raise the smog problem.
Key Causes of Smog in Los Angeles
| Cause | Contribution to Smog |
| High vehicle dependency | Over 7.5 million registered vehicles in LA County. |
| Warm climate | Promotes photochemical reactions. |
| Geography | Basin traps pollutants, preventing dispersion. |
Impacts of Smog
- Health: Higher rates of asthma among school-aged children; LA County is among the highest in California for asthma hospitalization.
- Economic: There are yearly healthcare costs totaling more than $14 billion due to smog in California.
Solutions Implemented
- Emission Standards: Using catalytic converters and standardizing severe emission laws.
- Public Transport Expansion: To minimize car use, transport investments in subways and buses.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Motives to own an EV: California Pradesh has placed ambitious targets and aims to sell only zero-emitting automobiles by 2035.
Results
There was a 50 percent reduction of smog-related ozone between 1980 and 2020 in LA, although there are still occurrences of high pollution days.
Case Study 2: Dehli India
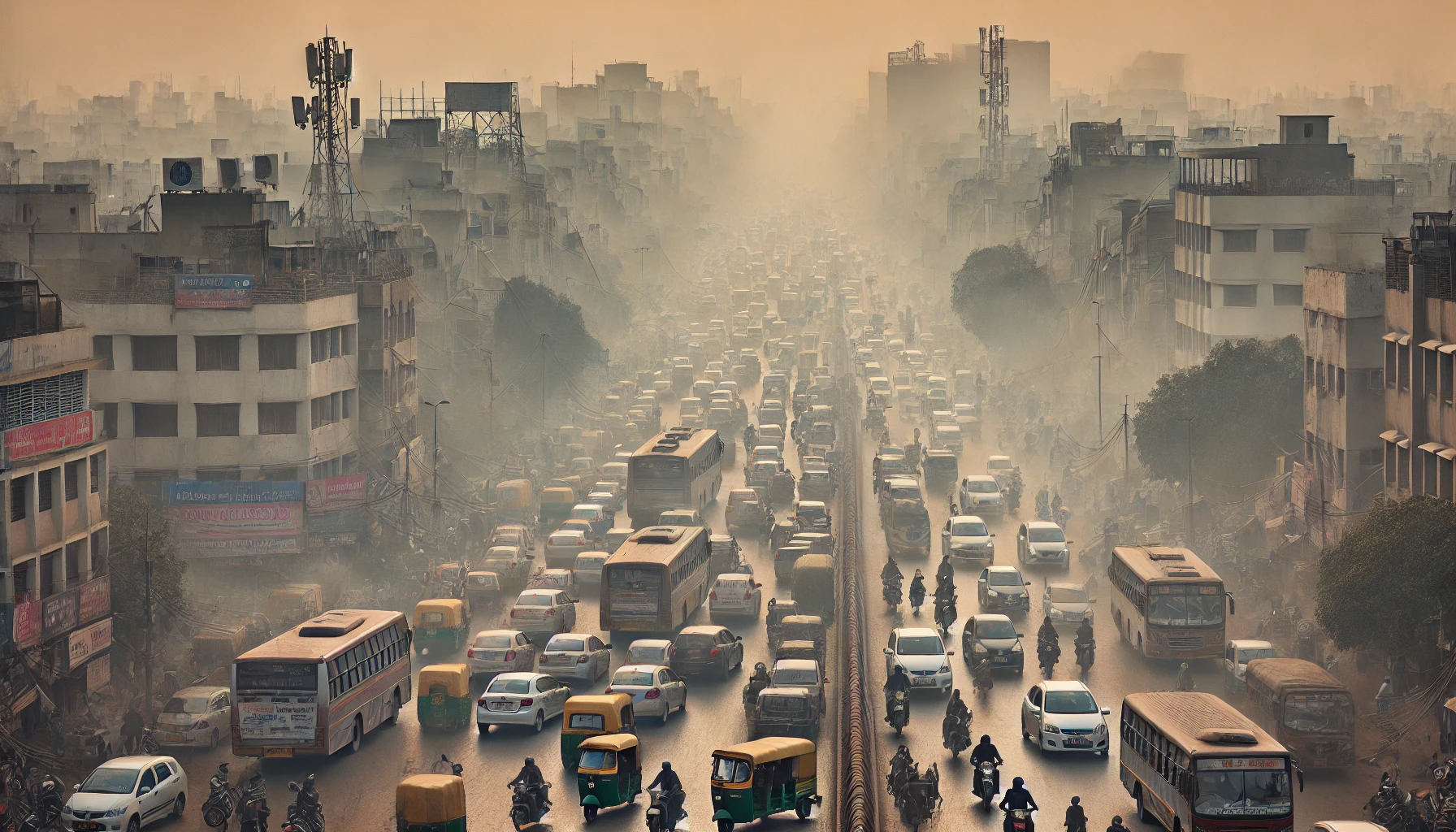

Overview
New Delhi, one of the most polluted cities globally, undergoes critical smog periods, especially during winter. Compounding the problem are emissions from automobiles, industrial effluents, and the burning of crops during the festive season.
Key Causes of Smog in Delhi
| Cause | Contribution to Smog |
| Diesel vehicles | Account for over 50% of NOx emissions. |
| Crop burning | Seasonal burning adds PM2.5 and PM10 to the air. |
| Overpopulation | Delhi’s population of over 30 million increases traffic density. |
Impacts of Smog
- Health: An estimated 2 million kids in Delhi have static scarring of the lungs because of pollution.
- Environment: Air pollution destroys the aerial part, affecting the underground water resources, particularly the Yamuna River.
Solutions Implemented
- Odd-Even Traffic Scheme: A system that replaces motion using the license plate numbers for automobile interchange.
- CNG Transition: CNG in buses and autos conversion for running is another example of using compressed natural gas.
- Electric Vehicles: The Delhi government provides a purchase subsidy of EVs; targets to have 25% of Ford EV vehicles on the road by 2024.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Establishing more than forty stations to monitor air quality within the city.
Results
Data shows that the annual PM2.5 levels in Delhi reduced by 15% between 2019 and 2023, but the data also shows that seasonal variation is still a threat.
Case Study 3: Beijing, China
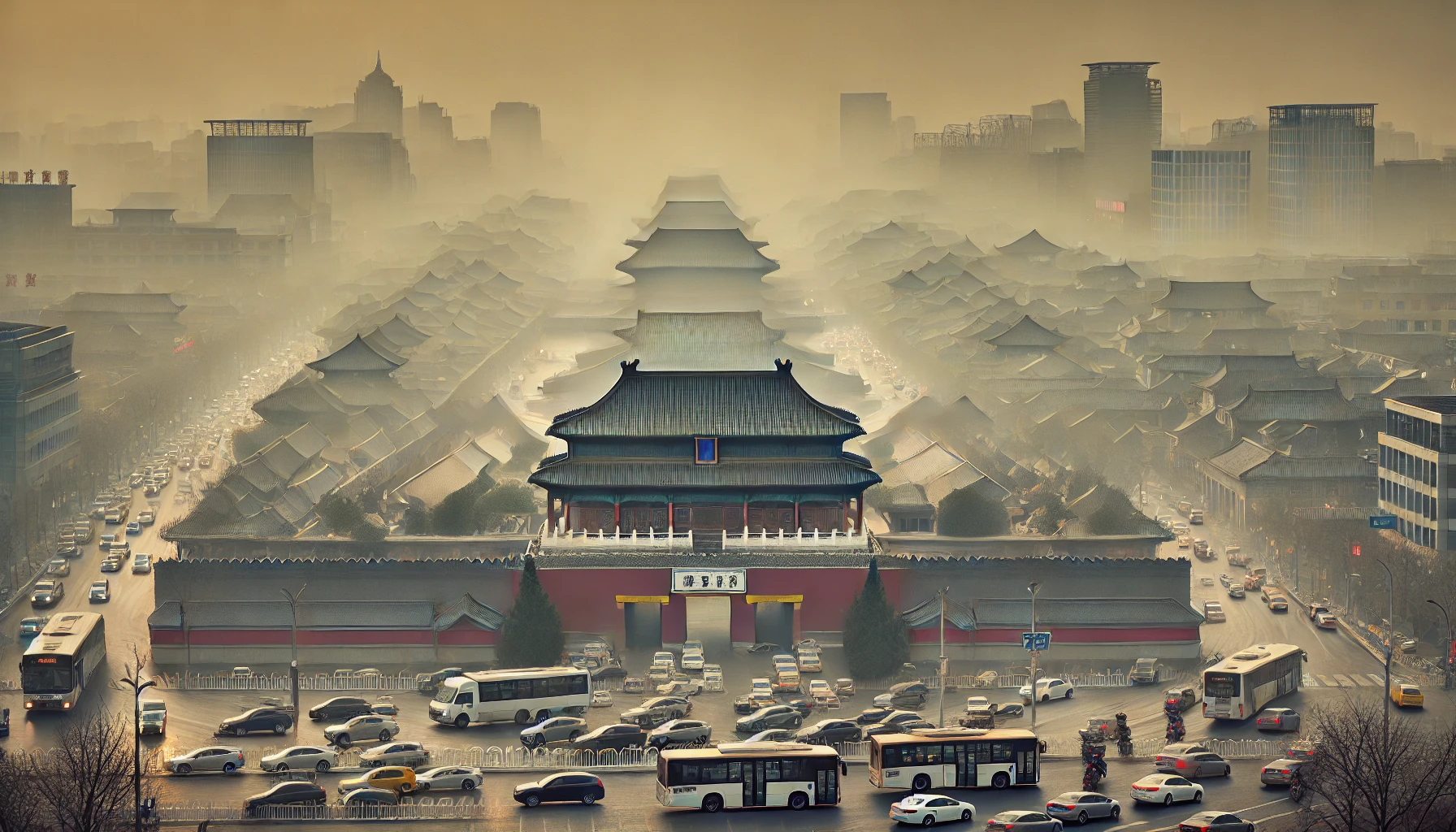

Overview
Beijing has become one of the most polluted cities because of its fast industrialization, but the Chinese capital has improved its air standards in the last 10 years.
Key Causes of Smog in Beijing
| Cause | Contribution to Smog |
| Vehicle emissions | Over 6 million cars contribute to smog. |
| Coal burning | Major energy source until recent transitions. |
| Geographic factors | Temperature inversions trap pollutants. |
Impacts of Smog
- Health: Due to pollution, Beijing residents die 6 years before their respective expected life expectancy.
- Economic: The economic costs for pollution-associated illness treatment and the impact on efficiency sum up to over thirty-eight billion dollars annually.
Solutions Implemented in Beijing
- Emission Reductions: Some policies include banning old-model vehicles and creating more substantial emission requirements.
- Public Transport Investment: Subway lines to be extended to 700 km.
- Electrification: Subsidy by the government to electric buses and taxis.
- Industrial Relocation: Big industries were shifted out of the urban areas.
Results
From 2013 to 2022, Beijing reduced its annual average PM2.5 by 35%, and the improvement is largely attributed to the central government’s determination to replicate exemplary measures such as those taken in other cities.
Measures to Prevent the Formation of Smog Due to Automobile Exhaust
Cities that suffer from smog caused by automobile emissions cannot just wake up one day and do what cities have done based on Congress. Here’s a roadmap:
Global Shift to Cleaner and Greener Fuels
Transitioning fossil fuels to cleaner fuels has significantly reduced vehicle emission rates.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Promote battery electric vehicle use with incentives and extending charging stations.
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): Use CNG in public transportation, as the Delhi transport department has done for bus services.
- Biofuels and Hydrogen: Source: Bold steps to promote bioethanol as an extended source of automotive fuels and hydrogen to facilitate energy diversity.
Invest in the Development of general transport networks
An efficient and affordable public transport system means fewer people using their cars.
- Metro and Subway Systems: Enlarge the networks to areas that cannot access networks. Beijing is one of the best examples where the metro is already expensive.
- Bus Rapid Transit (BRT): Busways to guarantee punctual and efficient bus transport.
- Bicycle Sharing: Encourage bike-sharing services to organize shared last-mile transportation.
Apply the Strict Standards of Vehicle Emission Control
Strict legislation can help reduce the emissions of undesirable contaminants.
- Adopt Euro 6 Standards: This pollution control strategy has been implemented well throughout many cities, thus achieving NOx and PM emissions under the stringent standards above.
- Retire Older Vehicles: Encourage people to trade in their vehicles with high emission rates for those with lower emissions.
- Regular Emissions Testing: Compulsory emission inspection ensures that environmental norms of the needed air quality are observed.
A paper titled Traffic Congestion Management Policies: An Introduction is suitable.
That has the direct effect of cutting back emissions from idling automobiles because it diminishes traffic.
- Congestion Pricing: Other city examples include London and Stockholm, where vehicle owners must pay a fee for access to congested parts of the city.
- As implemented in New Delhi, Odd-even policies involve restricting vehicle access based on license plate numbers during specified hours to combat high pollution levels.
- Smart Traffic Systems: F low control through artificial intelligence to avoid additional idle time.
Urban sustainability
Urban planning can help explain why many people drive long distances to work.
- Transit-Oriented Development (TOD): Organize neighborhoods around effective public transport interchanges.
- Mixed-Use Zoning: Group residential, commercial, and recreational functions to allow reduction of distances between them.
- Green Spaces: Create parks and plant street trees to remove toxic substances and to make the urban environment more extraordinary.
Promote The Use of Renewable Energy in Transport and Production
- Renewable Charging Stations: Power EV chargers through solar and wind technologies to minimize lifecycle emissions.
- Energy Transition Policies: Move people and goods via public transport and industries to renewable energy sources.
Develop Awareness and Educational Campaigns
Here, behavioral change is said to be central to addressing smog.
- Car-Free Days: Explain how to address the lack of car use by holding car-free activities.
- Community Involvement: Involve citizens in tree planting, exercise, and carpooling activities.
- Promote Eco-Driving: Educate consumers on how fuel efficiency is used and practiced on the road.
Implement Technology and Data Management
There are ways to monitor and control air quality through sophisticated equipment.
- Air Quality Monitoring Systems: Place real-time sensors throughout cities to identify the most polluted areas.
- Satellite Data: Create regional strategies for pollution based on satellite imaging of pollutants.
- Emission Reduction Apps: Environmental apps should be created that would enable the residents to calculate and reduce their carbon footprint.
Promote Electric and Shared Transport Service
- Incentivize EVs: They include personal income tax exemptions, loan interest rates, and free parking space for all EV owners.
- Carpooling Initiatives: Encourage carpooling by using UberPool or similar services where available or the like applications locally.
- Electric Public Transport: Replace public vehicles such as city buses and taxis with electrically powered machines.
Foster Regional and Global Collaboration
Pollution is not limited to certain city regions; it calls for unified action.
- Regional Cooperation: Engage other neighboring regions in combating the pollution source of the shared areas.
- Global Initiatives: One can join the C40 Cities and Clean Air Fund to get more support and information.
- Technology Transfer: Post progress on battery EVs, renewable power and energy, and better emissions management.
Case Study Examples
- Los Angeles, USA: Cutting smog by half through emission laws and dedicating resources to the development of public transportation.
- Beijing, China: Thanks to efficient measures such as industrial migration and public transportation development, a third of the PM2.5 has been cut in nine years.
- Singapore: Public transportation and congestion charging have considerably reduced emissions from instrumental transportation.
Global Smog Reduction Statistics
| Strategy | Estimated Reduction in PM2.5 Levels | Example Cities |
| Transition to EVs | 30–40% | Oslo, Shenzhen |
| Congestion Pricing | 15–20% | London, Stockholm |
| Metro System Expansion | 25–30% | Paris, Tokyo |
Conclusion
Traffic pollution in the form of vehicle emissions comprises a complex problem with catastrophic effects on health, the environment, and the economy. However, Los Angeles, Delhi, and Beijing prove that change is achievable with the help of the government, IT advancements, and the common people. With the urbanization rate increasing, so is air pollution, which may be a guideline for other cities. It is possible to dream of smokeless cities if countries adopt cleaner fuels, invest in public transport, and ensure that tough standards are implemented.
————————————————————————————————
Frequently Asked Questions
- Are cities polluted?
Yes, many cities worldwide experience pollution due to industrial activity, vehicle emissions, and population density.
————————————————————————————————
- What polluted cities?
Industrial waste, vehicular emissions, construction dust, and poor waste management cause city pollution.
————————————————————————————————
- What are the most polluted cities in the US?
As of recent data, Bakersfield and Los Angeles in California often top the list for air pollution in the U.S.
————————————————————————————————
- What are the most polluted cities in India?
Delhi, Kanpur, and Lucknow are among the most polluted cities in India, primarily due to industrial emissions and vehicle traffic.
————————————————————————————————
- What are the most polluted cities in Europe?
Cities like Kraków (Poland) and Sarajevo (Bosnia) are among the most polluted in Europe, mainly due to coal-based heating and industry.
————————————————————————————————
- What are the most polluted cities in North America?
In North America, cities like Los Angeles and Mexico City are among the most polluted, mainly from vehicle emissions and industrial activity.
————————————————————————————————
- Which are the least polluted cities in India?
Mysuru and Bengaluru are among the least polluted due to better environmental policies and green spaces.
————————————————————————————————
- Who polluted cities?
Urban pollution is primarily caused by human activities such as industrialization, transportation, and improper waste management.
————————————————————————————————
- Why are Chinese cities so polluted?
Rapid industrialization, coal dependency, and high population density pollute Chinese cities.
————————————————————————————————
- World’s most polluted city 2023
In 2023, Lahore, Pakistan, was frequently cited as the world’s most polluted city, with hazardous air quality.
————————————————————————————————
- World’s most polluted city 2024
As of December 2024, New Delhi, India, has been reported as the world’s most polluted city, with an Air Quality Index (AQI) reaching hazardous levels.
————————————————————————————————
- Top 10 most polluted cities in the world?
The top 10 most polluted cities often include New Delhi, Ghaziabad, and Gurgaon in India, Lahore in Pakistan, and several towns in Mongolia and Russia, based on real-time AQI data.
————————————————————————————————
- Top 10 most polluted cities in the world 2024
As of December 2024, the most polluted cities include New Delhi, Ghaziabad, and Gurgaon in India; Erdenet and Bulgan in Mongolia; and Irkutsk and Ulan Ude in Russia, according to real-time AQI rankings.
————————————————————————————————
- Most polluted country in the world?
Bangladesh has been reported as the most polluted country globally, with the highest average PM2.5 concentration levels.
————————————————————————————————
- Most polluted cities in Europe?
Iğdır in Turkey is considered Europe’s most polluted city, with PM2.5 levels over nine times the safe standard.
————————————————————————————————
- Most polluted city in Pakistan?
Lahore is the most polluted city in Pakistan, frequently experiencing hazardous air quality levels.
————————————————————————————————
- Worst air quality in the world today
As of 20 December 2024, New Delhi, India, has the worst air quality globally, with an AQI of 475, indicating hazardous conditions.
————————————————————————————————
Global Air Quality and Health Impacts
- World Health Organization (WHO):
- Reports on air pollution and its health impacts, including statistics on premature deaths caused by outdoor air pollution.
- WHO Air Pollution Overview
- World Bank:
- Studies on the economic costs of air pollution and mitigation strategies.
- World Bank – Air Pollution
Case Study – Los Angeles
- California Air Resources Board (CARB):
- Research on emission reductions in California and the impact of policies like vehicle emission standards.
- CARB Website
- South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD):
- Local air quality data and initiatives are specific to Southern California.
- SCAQMD Website
Case Study – Delhi
- Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India:
- Air quality reports, vehicle emission data, and policy updates for Delhi.
- CPCB Website
- The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI):
- Studies on the environmental impacts of pollution and sustainable urban planning.
- TERI Website
Case Study – Beijing
- China Air Quality Management:
- Insights into Beijing’s “war on pollution” and its policies on vehicle emissions and industrial relocations.
- China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment
- Peking University:
- Research on the effectiveness of Beijing’s pollution control measures.
- Relevant journals are available via university publications.
General Vehicle Emission Data
- International Energy Agency (IEA):
- Comprehensive reports on global trends in vehicle emissions and energy use.
- IEA Website
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), USA:
- Data on vehicle emissions, standards, and technologies to reduce air pollution.
- EPA Vehicle Emissions Page
Technology and Sustainable Transport
- International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT):
- Analysis of clean transport policies and the role of EVs in reducing emissions.
- ICCT Website
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Reports on sustainable mobility solutions and pollution reduction strategies.
- UNEP Air Quality Reports
Regional Air Quality Monitoring Tools
- AirVisual by IQAir:
- Real-time air quality monitoring for cities worldwide.
- IQAir Website
- World Air Quality Index (WAQI):
- Live data and trends for air pollution levels globally.
- WAQI Website
————————————————————————————————
A Comprehensive Guide to Honda Accord: A Timeless Choice for 2024 Car Buyers
Case Studies of Cities Heavily Impacted by Smog from Vehicle Emissions
Enhancing Air Quality and Comfort The Function of Climate Control Systems in Automobiles
Global Data – EV Tracking System & Emission Monitoring
Global Road Safety & Vehicle Standards_ A Complete Guide
Riding High – The Top 5 Vehicles Dominating 2024
Toyota Corolla 2024 Review – Everything You Need to Know About Features, Price, and Performance
The 15 Leading Startups Revolutionizing Autonomous Vehicles in 2024
The Evolution and Appeal of Sports Cars_ A Comprehensive Analysis
The Impact of Green Technology on the Automobile Industry
The Science Behind Car Safety Features_ How They Work
From Seatbelts to Sensors_ The Journey of Car Safety Innovations
How to Buy a Used Car_ A Step-by-Step Guide
We are a Trusted Name in Automotive Industry & Technologies!
Our Trusted Partners
We are proud to collaborate with industry leaders to deliver exceptional value and quality to our customers:
- Auto World Japan: A trusted name in exporting high-quality Japanese vehicles worldwide.
- BE FORWARD: A global leader in selling and exporting used cars with an excellent reputation.
These partnerships allow us to directly bring you reliable, top-tier services and products.